The Graphics Rendering Pipeline
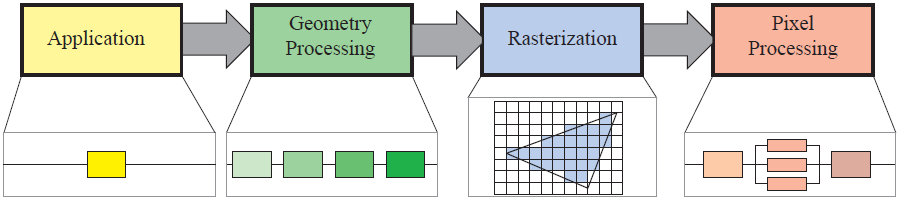
1. Application
- software
- CPU
- collision detection / global acceleration / animation / physical simulation / …
- not divide into substages -> executed in paraller -> superscalar construction
=>geometry / rendering primitives
2. Geometry Peocessing
- what / how / where
- GPU
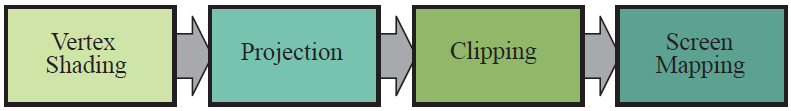
2.1 Vertex Shading
- compute the position for a vertex
- model -> world -> view / eye / camera
- evaluate vertex output data
- Vertex shading: compute a shading equation
2.2 Projection
- orthographic / parallel
- perspective
- view volume to unit cube -> project
- z coordinate -> stored in z-buffer, the models are projected from 3 to 2 dimensions
2.3 Clipping
- clip with unit cube -> clip
2.4 Screen Mapping
- 1x1 -> 1920x1080 -> screen/window
=>transformed and projected vertices with their shading data
3. Rasterization
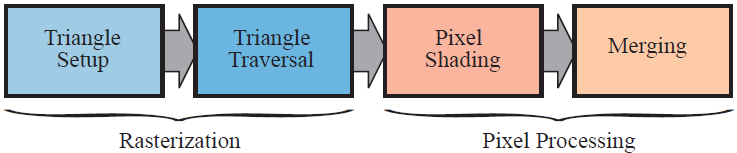
- triangle setup / primitive assembly
- triangle traversal
- find which samples or pixels are inside a triangle
- fixed function
- hardware
- triangles are formed from three vertices
=>fragment
4. Pixel Peocessing
- pixel shading
- programmable GPU core
- texturing
- merging
- highly configurable
- combine the fragment color with color buffer
- visibility
- alpha channel / stencil buffer / frame buffer /…
- double buffering
- different coordinates